
From India’s Toy Chest to the Trade Frontier
Once a toy importer that relied on foreign-made goods, India has changed dramatically. In recent years, it shifted from a domestic toy market that depended on imports to a global manufacturing player exporting to over 150 countries. However, as of August to September 2025, U.S. tariffs have disrupted this export story. They have affected established trade routes and raised costs for both manufacturers and consumers. This blog explores the history of India’s toy industry, its rapid growth, and the ongoing tariff conflict with the U.S. It highlights resilience in the face of economic challenges.
Chapter 1: Once Upon a Toy- India’s Trade Tale
India’s toy industry used to be fragmented, relying heavily on imports, mainly from China. According to The Economic Times and Organiser, between FY 2014 and FY 2023, exports increased by 239%, while imports dropped by 52%. This marked a significant change in India’s role in the global toy trade.
From FY 2019 to FY 2022, export values grew from ₹812 crore (about USD 112 million) to ₹1,237 crore (around USD 170 million). At the same time, imports fell sharply from ₹2,593 crore (approximately USD 358 million) to ₹819 crore (around USD 113 million).
By FY 2024, exports reached USD 152.34 million, slightly below the previous year’s USD 153.89 million. This suggests stabilization after a period of rapid growth. Meanwhile, imports dropped to about USD 65 million, a small part of the USD 235 million recorded in FY 2020. Dependence on Chinese toys decreased from 87% to 64% within four years.
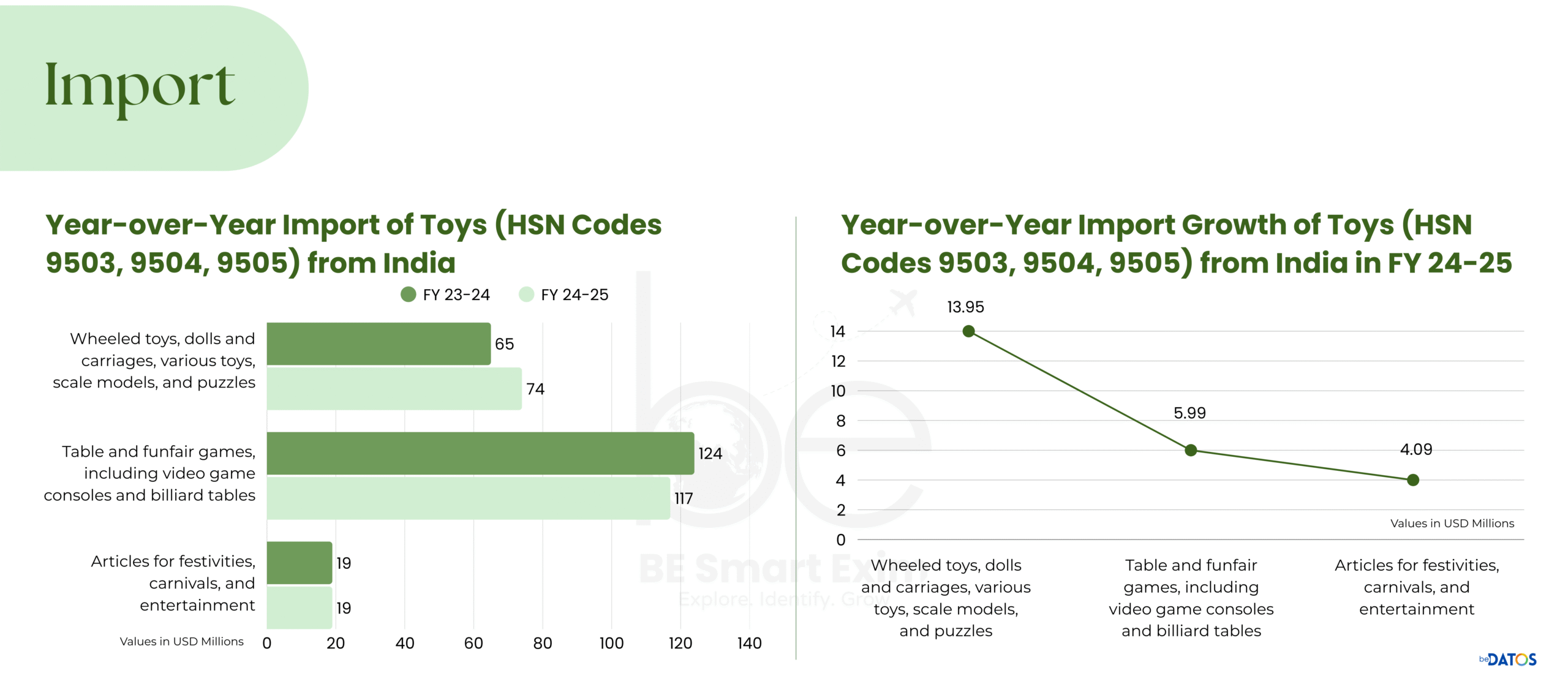
Source: beDATOS (SaaS; Trade intelligence platform), accessed September 2025.
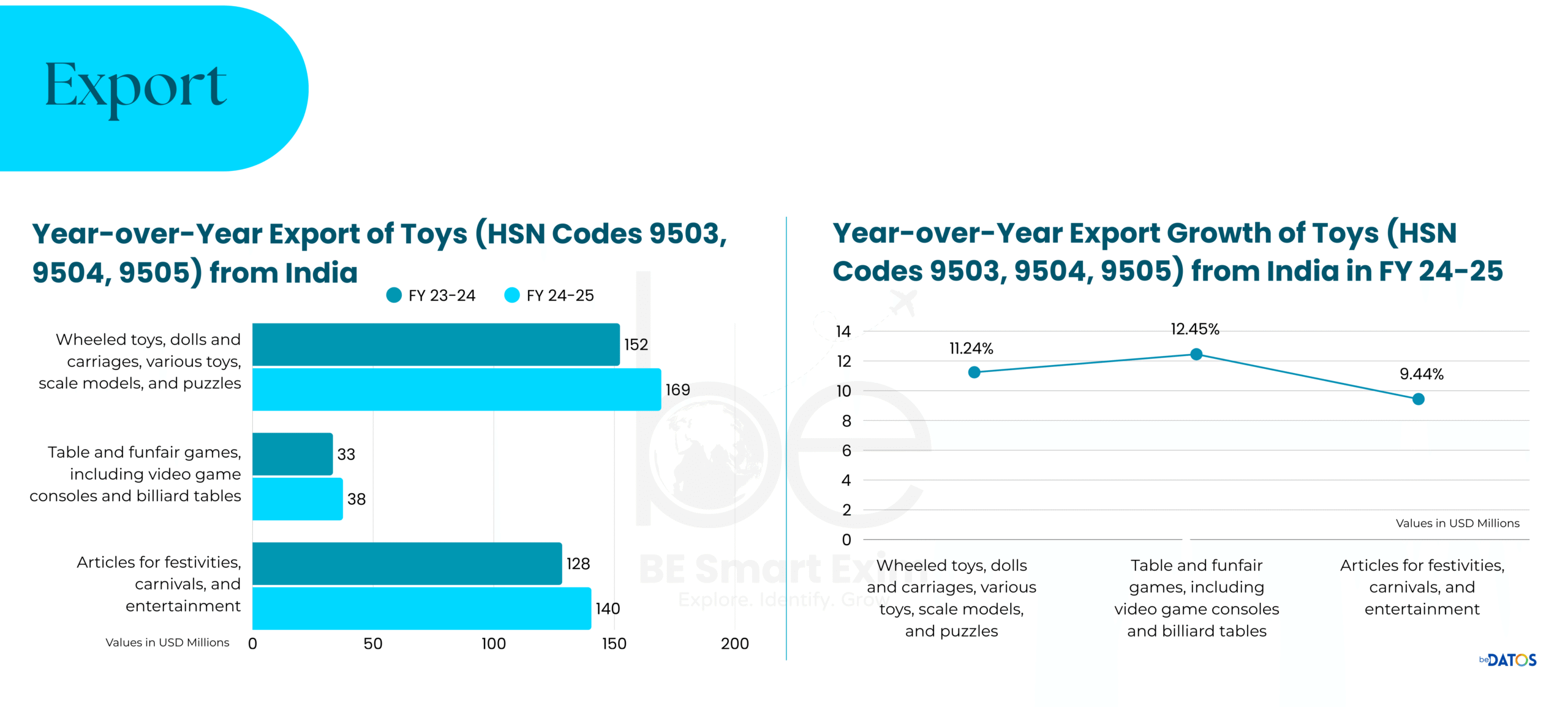
Source: beDATOS (SaaS; Trade intelligence platform), accessed September 2025.
The sharp drop in imports is mainly due to new policies like the Quality Control Orders (QCOs), updated tariffs, and the “Make in India” initiative. This initiative focuses on domestic production and stricter safety standards. Organized companies are primarily leading this change, while informal and traditional producers are struggling to keep up.
Chapter 2: Growth That Plays Well Globally
India’s toy industry didn’t just grow; it shifted focus to global markets with great ambition. At the Toy Biz International event in 2025, over 350 Indian toy brands showcased their products to more than 10,000 buyers from 25 countries, including major retailers like Walmart and Hamleys.
This expansion isn’t only about production; it’s also about outreach, branding, and meeting international safety and packaging standards. Analysts believe that India’s toy sector could reach USD 3 billion by 2028, driven by trade-friendly policies and increased global demand for safe and affordable toys.
Ten years ago, Indian toys were in only a few export markets. Now they reach over 153 countries. This international presence shows the investments made in quality control, packaging improvements, logistics, and partnerships that boost the sector’s global reputation.
Chapter 3: Tariff Tussle- When the U.S. Plays Rough
Just as India’s toy industry started to gain momentum, a tariff conflict with the United States put it in jeopardy. On August 7, 2025, the U.S. imposed a 25% tariff on Indian goods, including toys, citing concerns about the supply chain and ongoing geopolitical tensions.
Within weeks, this escalated to a 50% tariff by August 27, linked to sanctions over India’s oil imports from Russia. Analysts highlighted this as one of the most aggressive trade actions the U.S. has taken in recent decades.
This decision occurred during stalled trade talks and increasing diplomatic pressure, threatening the export-driven progress that Indian toy makers had worked hard to achieve.
Chapter 4: Tariff Tears- The Toll on Indian Toymakers
The tariffs have had a significant impact. The U.S. represents 47% of India’s toy exports, which makes it an essential market. Since the tariffs were implemented, exports to the U.S. have reportedly dropped by 8 to 10%. At the same time, prices for toys sent to American markets have increased by 5 to 7%. Some buyers, either unable or unwilling to handle the price rise, have shifted orders to other locations like Indonesia.
For many mid-sized exporters, these changes pose risks to both cash flow and reputation. The industry’s dependence on high-volume, low-margin sales means that even small disruptions can lead to longer-term instability.
Chapter 5: Response & Recovery- The Re-Shuffle Begins
Indian policymakers and industry groups are pushing back. The call to lower the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on toys from 12% to 5% shows the urgent need to remain competitive, both domestically and internationally.
Diplomatic efforts are in progress to create a multi-tier recovery plan that includes export incentives, market diversification, and possible actions at the World Trade Organization. A bilateral trade agreement with the U.S. is expected to be finalized by November 2025, according to the Commerce Ministry.
Meanwhile, Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s government has made targeted GST cuts on consumer goods, particularly those used in rural markets. This action aims to provide relief against rising inflation and supply issues, rather than act as a form of trade retaliation.
Turning Tariff Trial into Trade Triumph
India’s toy industry has come a long way. It has shifted from backyard workshops assembling cheap plastic imports to becoming a globally recognized manufacturing and export hub. The recent tariff actions by the U.S. have undoubtedly affected the industry, but the underlying infrastructure, including improved quality control, logistics, and branding, remains intact.
The next phase is critical. With strategic government support, targeted reforms, and new diplomatic channels, India has a chance to turn this tariff challenge into a trade victory. The focus will be on balancing cost, scale, and compliance while expanding into emerging markets that are less influenced by trade politics.
The industry’s story is one of resilience, ambition, and adaptation. Although tariff issues have created some uncertainty, the foundations for long-term global expansion are solid. India’s toy industry is determined to keep playing the game on its own terms.
Bibliography
beDATOS. (2025). India Toy Trade – Exports and Imports by Category (HSN 9503, 9504, 9505). SaaS platform. Retrieved September 2025.
Organiser. “Atmanirbhar Bharat and its Toy Story: How We Went from Importing to Exporting to 153 Countries in Just 8 Years.” Organiser, July 8, 2025. https://organiser.org/2025/07/08/301630/bharat/atmanirbhar-bharat-and-its-toy-story-how-we-went-from-importing-to-exporting-to-153-countries-in-just-8-years/.
ET Manufacturing. “From Imports to Exports: How India is Becoming a Global Toy Manufacturing Hub.” ET Manufacturing, n.d. https://manufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/fmcg/from-imports-to-exports-how-india-is-becoming-a-global-toy-manufacturing-hub/118643650.
ET Brand Equity. “India’s Toy Industry Sees Record Growth with 239% Rise in Exports by 2023.” ET Brand Equity, n.d. https://brandequity.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/marketing/indias-toy-industry-sees-record-growth-with-239-rise-in-exports-by-2023/121908936.
The Economic Times. “US Imposes 25% Tariff on India Products in Trade Dispute.” The Economic Times, August 7, 2025. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/foreign-trade/us-imposes-25-tariff-on-india-products-in-trade-dispute/articleshow/104530715.cms.
The Guardian. “US Imposes 50% Tariff on India Amid Trade Dispute.” The Guardian, August 28, 2025. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/aug/28/us-india-trade-war-tariffs.
Reuters. “US Imposes 50 Percent Tariff on India Over Russia Oil Imports.” Reuters, August 27, 2025. https://www.reuters.com/world/us-imposes-50-percent-tariff-india-2025-08-27/.
Wikipedia. “India–United States Trade Dispute.” Wikipedia, last modified September 2025. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/India%E2%80%93United_States_trade_dispute.
The Print. “US Tariff Hit: India’s Toy Exports Down 10%.” The Print, September 5, 2025. https://theprint.in/economy/us-tariff-hit-india-toy-exports-down-10-percent/1325432/.
The New Indian Express. “US Tariff Hits India Toy Exports’ Growth.” The New Indian Express, September 5, 2025. https://www.newindianexpress.com/business/2025/sep/05/us-tariff-hits-india-toy-exports-growth.html.
The New Indian Express. “India Toy Sector Urges GST Reduction to Stay Competitive.” The New Indian Express, September 10, 2025. https://www.newindianexpress.com/business/2025/sep/10/india-toy-sector-urges-gst-reduction-2447705.html.
The Times of India. “India Plans Global Outreach After US Tariff Blow.” The Times of India, n.d. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/india-plans-global-outreach-after-us-tariff-blow/articleshow/104674321.cms.
Reuters. “India–US Trade Deal Expected by November 2025.” Reuters, September 1, 2025. https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/india-us-trade-deal-november-2025-2025-09-01/.
The Times of India. “Modi Government Targets Rural Demand with GST Cuts.” The Times of India, n.d. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/modi-government-targets-rural-demand-with-gst-cuts/articleshow/104590112.cms.

